If you're a developer working with Laravel, you've likely felt the thrill of using an AI coding assistant like GitHub Copilot or ChatGPT. You've also probably felt the frustration when it generates code that's almost right. It might use an old, deprecated function, invent a class that doesn't exist, or completely miss the unique structure of your project. We've all been there, trying to prompt our way out of a syntactical dead end.
This is the "context problem." General-purpose AI is powerful, but it's like a brilliant developer who has never seen your codebase. It doesn't know your specific Laravel version, your database schema, or the exact dependencies you have installed.
Enter Laravel Boost, the official AI coding starter kit designed to solve this exact issue. It doesn't aim to replace your favorite AI assistant; it makes it exponentially better. Boost acts as a "context bridge," giving your AI a real-time, structured understanding of your application and turning it from a generic code generator into an expert assistant with intimate knowledge of your project.
What is Laravel Boost?
Announced at Laracon US, Laravel Boost is built on three core pillars that work together to provide comprehensive, real-time context to your AI agent. It's a free, open-source package that enhances the tools you already use, like those in VS Code, PhpStorm (Junie), and Cursor.
Let's break down how it works.
The Three Pillars of Laravel Boost
- The Laravel-Specific MCP Server: At its core, Boost runs a server inside your project that uses the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an open standard for AI-to-tool communication. This server gives the AI over 15 specialized tools to programmatically inspect and interact with your live application. It can check your database schema, list your routes, or even execute code via Tinker to understand the real state of your app.
- The Vectorized, Version-Specific Documentation API: Boost connects your AI to a massive knowledge base of over 17,000 documentation entries from the entire Laravel ecosystem (including Livewire, Inertia, Filament, and more). The crucial part is that it's version-specific. The AI can retrieve documentation that matches the exact versions of the packages in your
composer.jsonfile, dramatically reducing errors from outdated or hallucinated code. - The Curated, Laravel-Maintained AI Guidelines: Boost installs a set of instruction files into your project that guide the AI on how to behave. Curated by the Laravel team, these guidelines enforce framework conventions and best practices. They can also prompt the AI to perform value-added tasks it might otherwise skip, like writing a feature test for the code it just generated, which is a massive win for code quality.
Here's how these pillars work together to elevate your AI-assisted development experience.
| Feature | Purpose | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Laravel-Specific MCP Server | To give AI agents programmatic tools to inspect and interact with the live application state. | AI can base its actions on reality (your actual DB schema, routes, and config) instead of guessing. |
| Vectorized Documentation API | To provide the AI with a searchable knowledge base of version-specific Laravel ecosystem documentation. | AI generates code using the correct, up-to-date APIs for your project's dependencies, reducing errors and hallucinations. |
| Curated AI Guidelines | To instruct the AI on how to behave, enforcing Laravel conventions and best practices. | AI-generated code is more idiomatic, follows project style, and includes crucial steps like writing tests, improving overall quality. |
Installation and Configuration
Getting started with Boost is incredibly simple. It's a development dependency you can pull in with Composer.
First, open your terminal in a Laravel project and run the following command:
composer require laravel/boost --dev
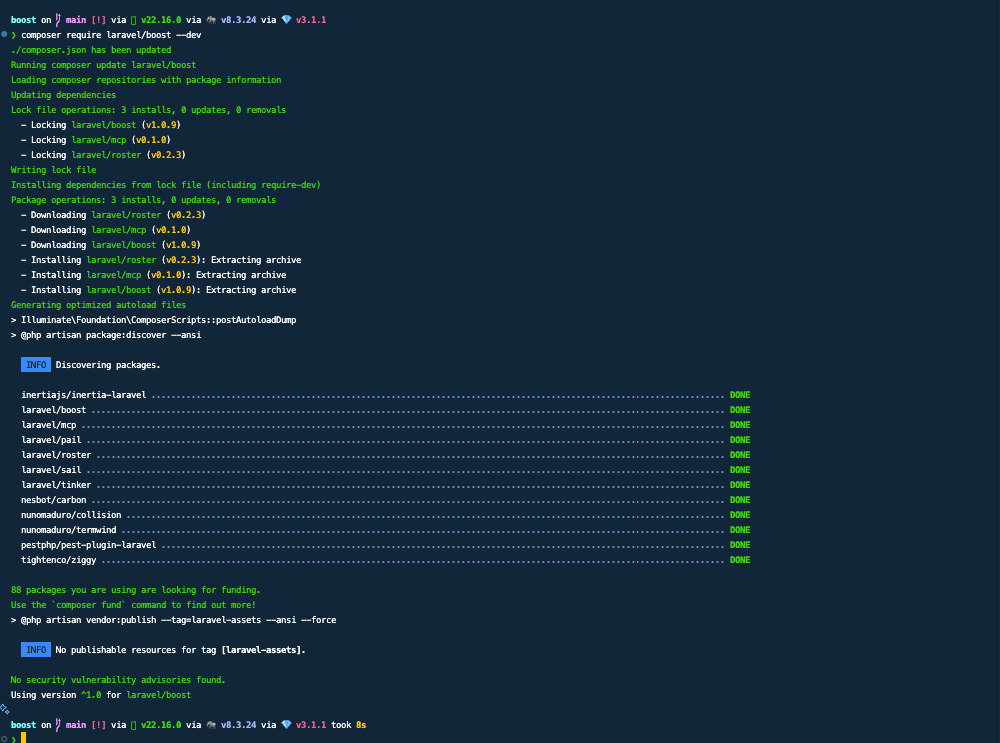
Next, run the boost:install Artisan command:
php artisan boost:install

You'll be greeted by a smart, interactive installer. This installer asks which AI client you use (like Cursor, PhpStorm, etc.) and what guidelines you want to install. This gives you complete control over the setup—it's not "magic," it's smart, transparent configuration.
Use the space bar to select which IDEs and AI clients you want to configure, then press enter to choose which agents get the AI guidelines.

You're now ready to use Laravel Boost.

Getting Started: Your First Prompts
Once Boost is installed, it works seamlessly in the background. Open your IDE's AI chat panel and start asking questions. The key is to talk to your application through the AI. Instead of asking "How do you create a route in Laravel?", you can now ask "What routes does this application have?".
Here are a few prompts to get you started.
1. Inspect Your Application's State
Try asking the AI for information about your project's environment. This is a great first test to see if Boost is working.
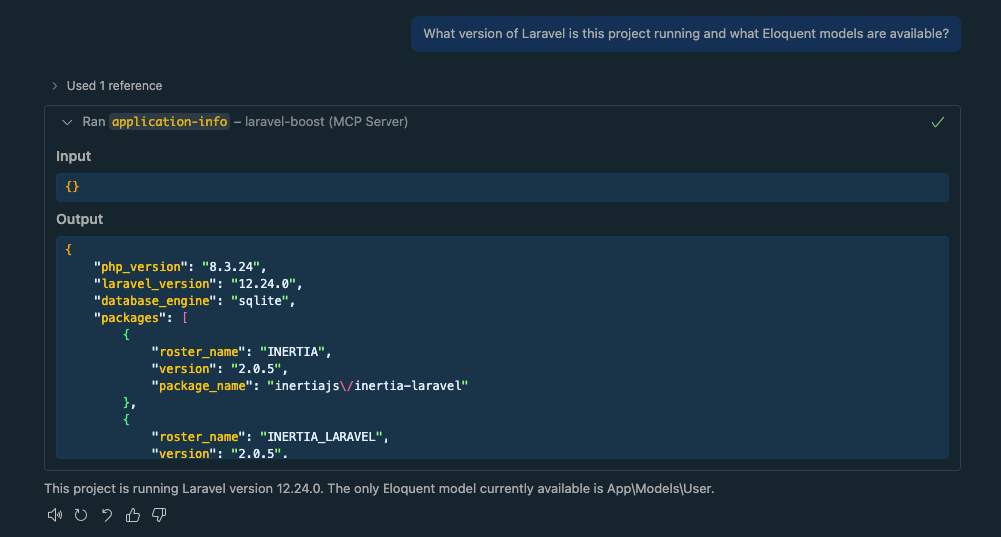
Prompt: "What version of Laravel is this project running and what Eloquent models are available?"
The AI will use the application-info tool to read your project's state and give you a precise answer, not a generic one from public training data.
2. Explore Your Database
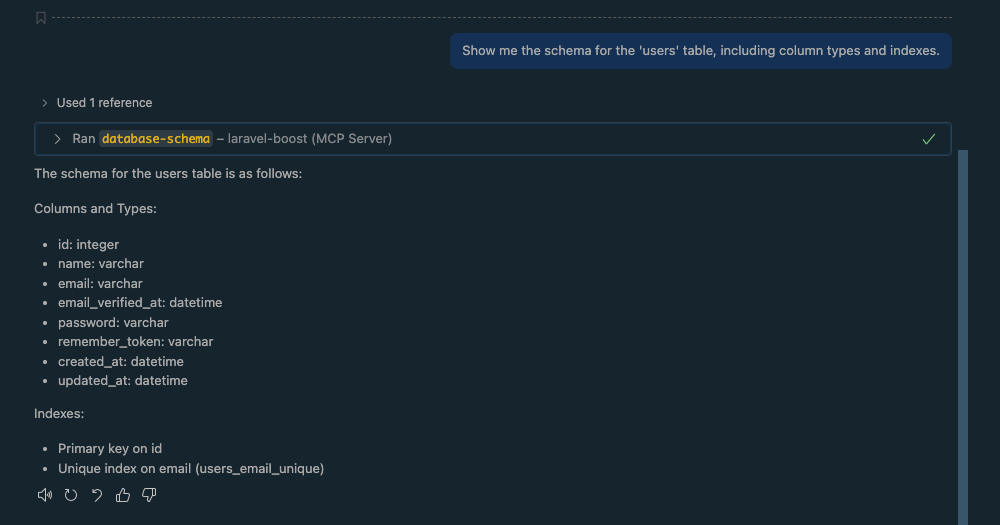
Before you write a single line of code, you can explore your database schema. Assuming you have a users table, try this:
Prompt: "Show me the schema for the users table, including column types and indexes."
Boost's db-schema tool will fetch and display the exact structure of your table.
3. Search the Right Documentation
Struggling to remember the syntax for a specific feature in your version of Laravel? Let the AI find it for you.
Prompt: "Search the docs for how to create a custom validation rule in Laravel 12."
The AI will use the search-docs tool, which is connected to the version-specific documentation API, to provide a relevant and accurate code example. When searching the docs for the first time, your AI agent might ask you for confirmation:
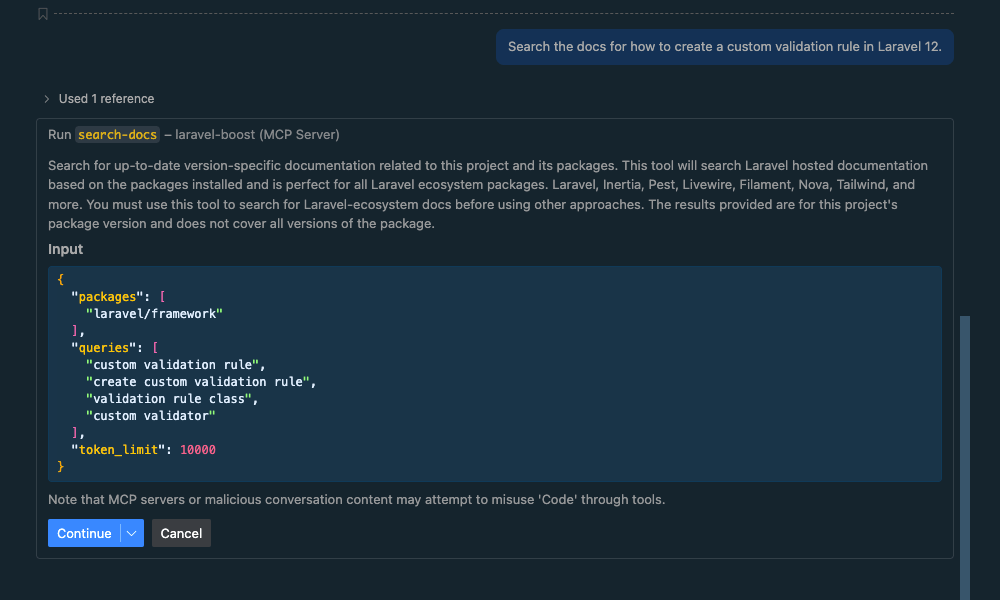
Upon confirmation it will search the docs:
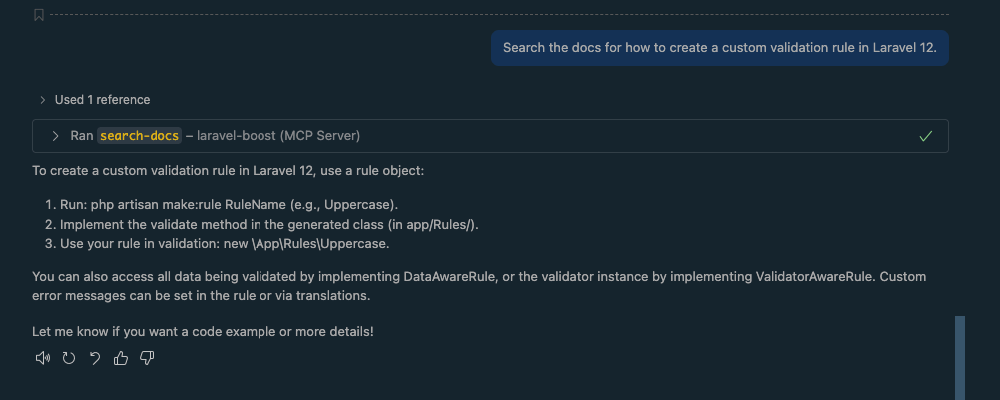
4. Debug an Error
If you run into an error, you don't have to leave your IDE. You can ask the AI to check the logs for you.
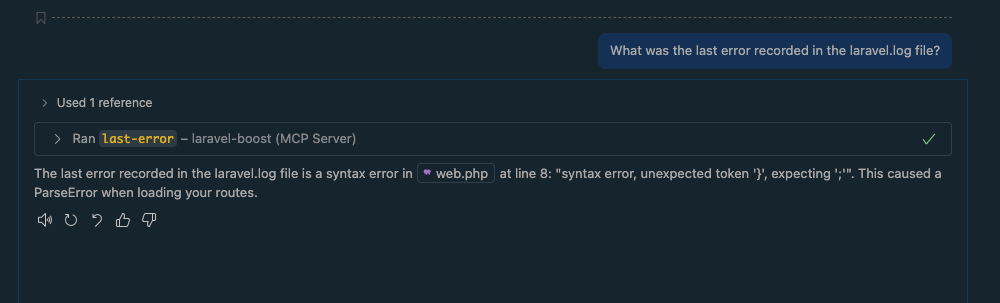
Prompt: "What was the last error recorded in the laravel.log file?"
This uses the last-error tool to pull the latest exception directly from your log file, allowing you to debug right from the chat panel. There are many more tools available that will give your AI more context and make you more productive in Laravel projects.
Deep Dive: The MCP Server Toolkit
The engine that powers Boost's interactive capabilities is the MCP server. Here is a comprehensive reference table of the tools it makes available to your AI assistant. Understanding these tools will help you craft even more powerful and precise prompts.
| Tool Name | Function Description | Example AI Prompt |
|---|---|---|
application-info |
Read PHP and Laravel versions, packages, models. | What version of Laravel is this project running and what Eloquent models are available? |
browser-logs |
Read logs and errors from the browser. | Check the browser logs for any recent errors. |
db-connections |
Inspect available database connections. | What is the default database connection for this app? |
db-query |
Execute a query against the database. | Run a SQL query to count the number of users in the users table. |
db-schema |
Read the database schema. | Show me the schema for the tasks table, including column types and indexes. |
get-absolute-url |
Convert relative path URIs to absolute URLs. | Generate a full URL for the /dashboard path. |
get-config |
Get a value from configuration files. | What is the value of app.timezone in the config? |
last-error |
Read the last error from the application's log files. | What was the last error recorded in the laravel.log file? |
list-artisan-commands |
Inspect the available Artisan commands. | List all available Artisan commands related to the queue. |
list-available-config-keys |
Inspect available configuration keys. | What configuration keys are available under the database.connections.mysql namespace? |
list-available-env-vars |
Inspect available environment variable keys. | List all the environment variables that start with VITE_. |
list-routes |
Inspect the application's routes. | Show me all the POST routes defined in the application. |
read-log-entries |
Read the last N log entries. | Read the last 10 entries from the application log. |
report-feedback |
Share feedback about Boost with the Laravel team. | Give Boost feedback: The search-docs tool was incredibly helpful for finding the new Mail syntax. |
search-docs |
Query the version-specific documentation API. | Search the docs for how to create a custom validation rule in Laravel 12. |
tinker |
Execute arbitrary code within the context of the application via Tinker. | Use Tinker to create a new User with the email test@example.com and password password. |
Conclusion and What's Next
Laravel Boost fundamentally changes our relationship with AI coding assistants. By solving the context problem, it leads to higher-quality code, fewer frustrating errors, and a dramatically improved developer workflow. Because it's a free, open-source package, you can start benefiting from it today.
To get started, check out the official repository on GitHub:
- Laravel Boost on GitHub: https://github.com/laravel/boost
This is just the beginning of what's possible. Now that you have Boost installed, the next step is to start integrating it into your daily coding habits. Stay tuned for our next post, where we'll walk through building a complete feature from start to finish.